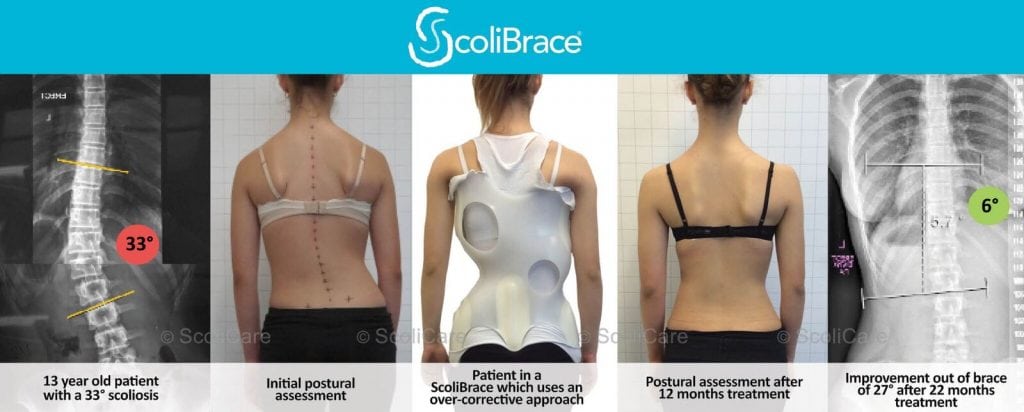
This month, the UK Scoliosis clinic is raising awareness about Scoliosis in adults, as part of our work for Scoliosis awareness month. Over the last few weeks, we’ve looked at the kinds of scoliosis that impact adults, and older adults in particular. This week, we’ll take a look at how you can recognise the signs and symptoms of Scoliosis, as an adult.
Recap : Scoliosis in adults
There are two main types of adult scoliosis. Pre-existing adult scoliosis is essentially a case of scoliosis which is continuing from an earlier age (usually adolescent scoliosis). In adulthood, a continuing case of scoliosis typically becomes known as Adolescent Scoliosis in Adults or ASA. ASA can be discovered in adults of any age, but many ASA cases are already known from treatment earlier in life. While many Scoliosis cases which are carried into adulthood progress very slowly (and may not progress at all for some time if they are small enough at skeletal maturity)[1] cases can begin to worsen again as we age and the spine (particularly the intervertebral discs) start to degenerate. Accordingly, worsening scoliosis in an ASA case is often referred to as Adult Degenerative Scoliosis.
The second type is Degenerative De-Novo Scoliosis (sometimes noted as DDS) – this is the development of a new scoliosis case, usually as a result of spinal degeneration – the cause is essentially the same as degeneration in ASA, however, we usually refer to De-Novo separately, since there is no prior history of Scoliosis. This being said, it may not always be possible to disambiguate a De-Novo case from an ASA case, since the lack of detection of a scoliosis case does not equate to the absence of scoliosis itself!
Adult Scoliosis – General signs
Not all signs of Scoliosis, especially in adults, are of the specific kind which tend to be noticed in children and younger teenagers – in fact, many adult scoliosis cases are discovered as a result of an investigation for back pain rather than concerns about Scoliosis.
Adults with scoliosis very often experience more generalised symptoms than younger people, due to the degeneration of the spinal discs and joints also taking place – this commonly leads to the narrowing of the openings for the spinal sac and nerves, a condition called spinal stenosis which can range from uncomfortable to extremely painful.
Many patients with adult scoliosis may adopt unusual postures in an attempt to avoid and reduce this pain – some patients with adult scoliosis may lean forward to try and open up space for their nerves. Others may lean forward because of loss of their natural curve (lordosis, sway back) in their lumbar spine (low back). The imbalance causes the patients to compensate by bending their hips and knees to try and maintain an upright posture.
Accordingly, back pain, and specifically Low back pain and stiffness are common issues for those with adult scoliosis. Numbness, cramping, and shooting pain in the legs due to pinched nerves, as well as fatigue resulting from strain on the muscles of the lower back and legs are all common issues.
Finally, while not a diagnostic indicator, it is worth noting that many older adults may also experience arthritis, which commonly affects joints of the spine and leads to the formation of bone spurs.
Adult Scoliosis – Traditional symptoms
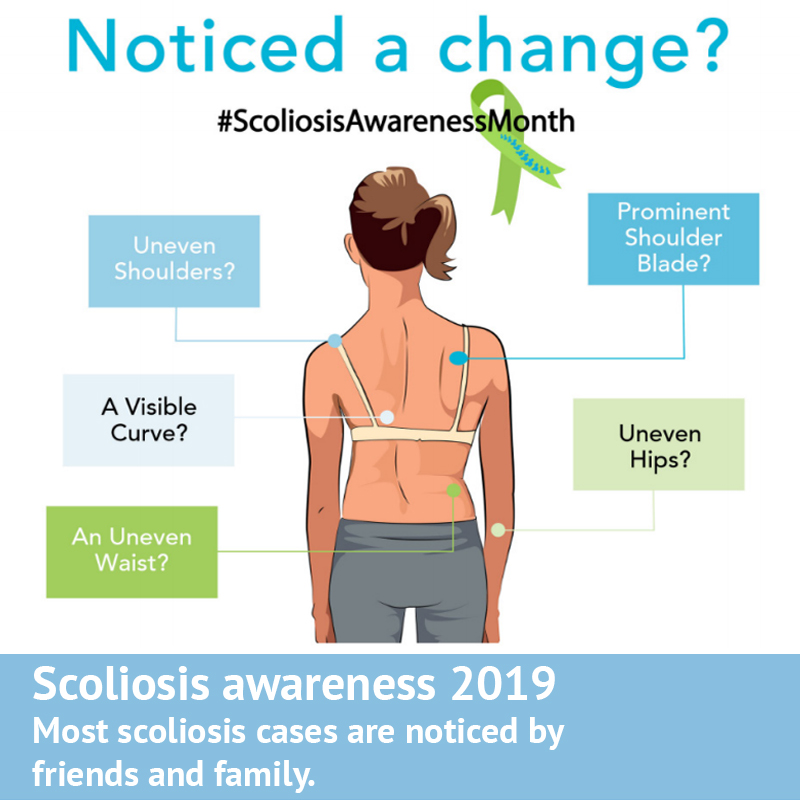
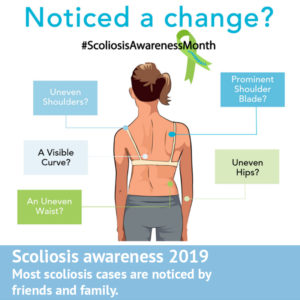
The more traditional, physical symptoms associated with scoliosis of course also apply to adult cases, and it’s these which are easiest to screen for.
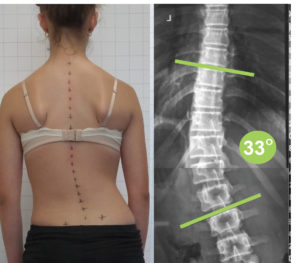
Degenerative Scoliosis linked to ASA can often occur in the thoracic (upper) and lumbar (lower) spine, with the same basic appearance as that in teenagers, such as shoulder asymmetry, a rib hump, or a prominence of the lower back on the side of the curvature.
De-Novo cases are typically seen more in the lumbar spine (lower back) and are usually accompanied by straightening of the spine from the side view (loss of lumbar lordosis).
Home Screening for Scoliosis
While the more general, painful symptoms are best investigated by a spinal professional (whether scoliosis is the cause or not), a basic home screening for the physical signs of scoliosis is easy to do. Simply follow the steps here!
[1] Weinstein SL, Ponseti IV: Curve progression in idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1983, 65:447-455.