If you have recently discovered that your child has scoliosis, or you suspect that scoliosis might be an issue it can often be a stressful and confusing time. There is a great deal of new information to consider and often it can seem there simply isn’t enough time.
If you have recently discovered that your child has scoliosis, or you suspect that scoliosis might be an issue it can often be a stressful and confusing time. There is a great deal of new information to consider and often it can seem there simply isn’t enough time.
To help out with this, here’s out top 10 list of things that you should do when first considering scoliosis treatment. Get these 10 done, and you’ll be well on your way!
1 – Screen for scoliosis at home
If you have already had your child screened for scoliosis, either at home or by a professional you can skip this step. If you have not yet performed a scoliosis screening however, begin here.
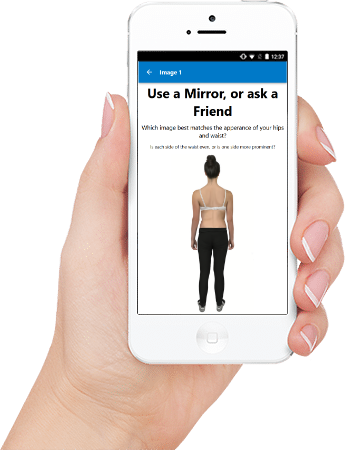
Scoliosis screening is easy to do at home using our ScoliScreen tool. ScoliScreen was developed in Australia by our partner ScoliCare, who spent years researching and designing the easiest home screening tool available. Screening with ScoliScreen takes about 10 minutes – you don’t have to take any pictures or upload any information, just follow the steps on screen and note down your results. ScoliScreen isn’t an alternative to a professional consultation, but it’s a highly effective tool to use as a starting point.
2 – Get a professional consultation
Screening and consultations are always available at the UK Scoliosis Clinic
We can’t stress enough that getting a professional consultation with a scoliosis specialist is a must. Many parent’s natural reaction is to take their child to see their GP about their concerns– but this isn’t always the best step.
There are a few reasons for this – Firstly, while no question that GP’s do fantastic work, with so many different conditions to recognise and treat most GP’s simply don’t have time to research the latest options for scoliosis treatment. Years ago, it was thought that surgery was the only effective option for treating scoliosis, so many medial professionals were simply taught that the best approach to scoliosis is to “wait and see” if the curve becomes bad enough for treatment. The problem is that scoliosis almost never resolves on its own[1] so “wait and see” is never a good option. If your GP tells you to “wait and see” please bear in mind they aren’t trying to be dismissive, they just aren’t experts on the non-surgical options which are available today (but scoliosis clinicians are!).
Secondly, properly diagnosing scoliosis requires taking X-rays to fully understand the position of the spine – since GP’s have to justify any referral it can be difficult to argue for x-rays to be taken when “wait and see” is the standard recommendation.
Finally, scoliosis has often been a condition which hasn’t received the attention it really should, so many people think that the GP is their only option. One child in each class at school will develop scoliosis[2], so a significant number of people are affected, but most people are unaware of the condition. If you are reading this blog as a first port of call, please know there are numerous specialist clinics out there waiting to help!
At the UK Scoliosis Clinic, scoliosis screening as well as consultations for those with scoliosis are always available.
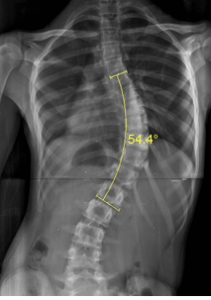
3- Get X-rays
Scoliosis is a complex Three Dimensional condition which can be successfully treated only with a thorough understanding of the condition of the spine. X-rays are the best way to properly establish the situation and also to rule out any other underlying conditions which might be causing or contributing to scoliosis. At the UK Scoliosis clinic, we have a brand-new state of the art digital X-ray machine on site for instant results – other clinics might refer you to another provider to get X-rays taken in advance of your consultation.
Some clinics offer what is often marketed as “radiation free imaging” – this simply means they do not provide X-rays and use an alternative, less effective imaging method. In real terms, this means that practitioners simply cannot get as good a picture of what is going on with the spine, which increases the risk of treatment failure, misdiagnosis or even injury from inappropriate treatment.
Are X-rays dangerous? The short answer is a handful of X-rays are far less risky than requiring major spinal surgery due to failed scoliosis treatment. The longer answer is that in fact, we are all exposed to a small amount of background radiation everyday without ill effect. For context, an average lumbar X-ray exposes you to only about as much radiation as 2 months of normal background radiation in the UK. An average airline pilot is exposed to about an eighth as much radiation as an x-ray on each transatlantic flight, meaning that most pilots are exposed to about the same amount of radiation as found in your x-ray every other week.
4 – Understand your treatment options

Specialist exercises can reduce Scoliosis
Today the non-surgical scoliosis treatment field is growing fast and there are many different approaches which can be utilised, these include treatments backed up by extensive research, such as Schroth and SEAS exercise methodologies and bracing as well as some emerging approaches which might or might not be effective, but currently lack enough research – such as chiropractic approaches.
Many clinics, like the UK Scoliosis Clinic offer a range of treatments and will tailor your treatment options based upon your needs, but some clinics only offer one approach. In this case, be sure that the treatment being offered is actually the right one for your case – and get a second opinion if you feel unsure.
5 – Chose a clinic which conforms to the SOSORT guidelines
Like all professions, the scoliosis treatment field has a guiding body – for us it’s the International Society on Scoliosis Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Treatment, otherwise known as SOSORT. SOSORT is an International organisation that guides health professionals on the most up to date, evidence-based recommendations in relation to the conservative treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. SOSORT’s ongoing mission is to constantly evaluate new treatment methodologies and to publish guidelines for best practice for patient outcomes[3].
Reputable clinics are run by clinicians who follow the SOSORT guidelines and stay in touch with the latest research – check that your clinician is keeping up to date by attending the yearly conference or contributing to the journal for example.
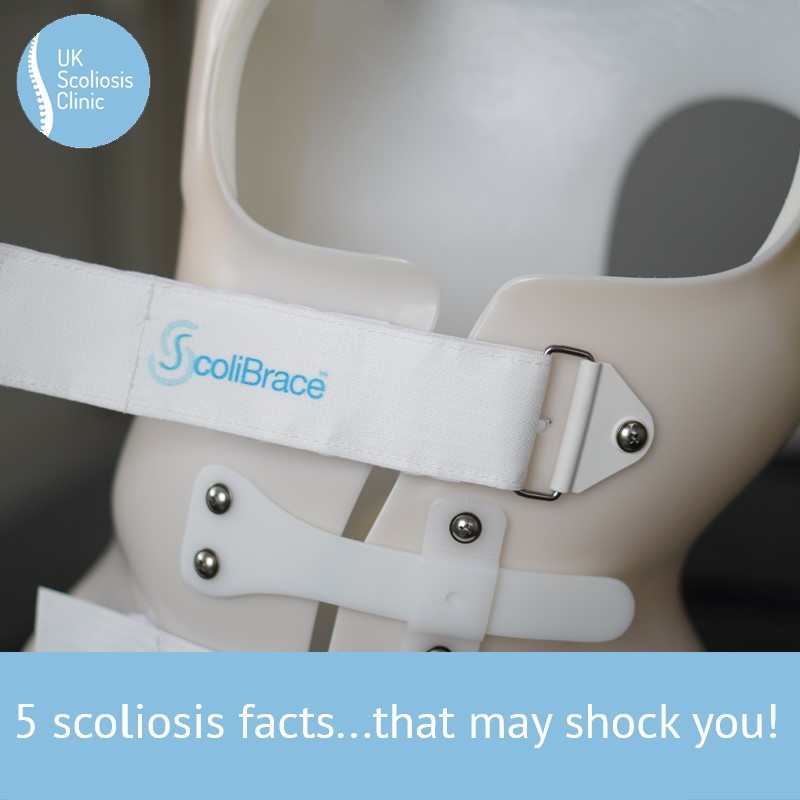
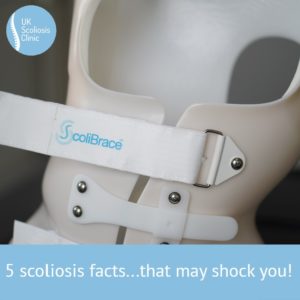
6 – Get the best brace
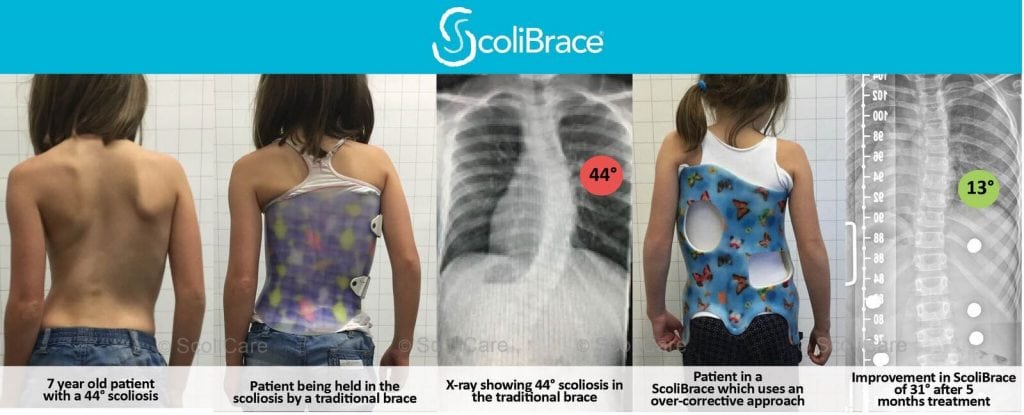
In many cases, bracing is going to be the most effective, fastest and easiest way to correct scoliosis. However, not all braces are created equal – be sure to quiz your scoliosis care provider about the braces they offer and the features they provide. Many braces (including those available in some areas through the NHS) are designed to hold the spine in its already scoliotic position. This kind of brace might stop the scoliosis progressing, but it wont help to improve it.
At the UK Scoliosis Clinic, we recommend ScoliBrace – a totally custom brace designed with 3D imaging and computer aided design. The ScoliBrace is an active correction brace – meaning it actually guides the spine back into the correct position, rather than just holding it still.
7 – Consider mental health
While everyone’s scoliosis experience is varied and depends much upon personality, some research has shown that children and young adults are more at risk of stress and even depression as a result of scoliosis. At the UK Scoliosis clinic, we provide a private one to one environment, and welcome as many relatives or friends that your child would like to have around them. Research has shown that having a calming and private environment to discuss and perform treatment can actually lead to better clinical outcomes[4].
When considering bracing, try to also take into account the impact wearing a brace could have on a young person’s life. This is one of the reasons we are so confident in our ScoliBrace – unlike many braces ScoliBrace is low profile and is easily hidden under normal clothes. Additionally, ScoliBrace does not impede a child’s ability to participate in sports and physical activities and was designed specifically with maximising mobility in mind. ScoliBrace is also customisable in a range of colours and patterns to suit your tastes!
8 – Ask questions

Dr Paul Irvine and Dr Jeb MacAviny at the SOSORT conference 2018
Ask questions, ask lots of questions – and encourage your child to ask questions. A scoliosis consultation appointment is a great opportunity to do this, but feel free to phone our clinic for more information. Scoliosis treatment is a fast-moving field in which new research is always being published, so as scoliosis clinicians we spend much of our time asking questions and keeping up with research too. Avoid a clinic who can’t (or wont) answer your queries and opt for one that shows they are up to date with the latest information.
Whenever you speak with a scoliosis practitioner, consider making a list of things you would like to know and make sure you get answers! Reputable clinics will be able to answer any queries you may have, and back these answers up with the latest published scientific research papers.
9 – Consider the cost of treatment carefully
When considering the cost of scoliosis treatment, its important to remember that a scoliosis treatment program is not a “quick fix” – time is required to initially correct scoliosis, and then further maintenance treatment of some kind is then required to keep the spine properly aligned until the end of growth. This means that parents need to ensure that the treatment options they choose represent a sensible choice over the long term. To give an example, this might mean that a more expensive scoliosis brace, which is adjustable to last for a long period of time may be more cost effective than two or three cheaper braces. Similarly, for small curves a ScoliNight brace might be a better long-term investment than continued scoliosis specific exercise sessions.
This decision depends to a great extent upon your own preferences and your child’s– but keep the long term in mind.
10 – Get on with your life!
Scoliosis does not need to be an impediment to life – and if treated properly and early on can usually be corrected without any serious impact on the young person concerned. If properly treated and corrected scoliosis will not affect your child’s life going forward, so plan for tomorrow!
[1] Angelo G Aulisa et al. ‘Brace treatment in juvenile idiopathic scoliosis: a prospective study in accordance with the SRS criteria for bracing studies – SOSORT award 2013 winner, Scoliosis 2014 9:3
[2] Gutknecht S, Lonstein J & Novacheck T ‘Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Screening, Treatment and Referral’ 2009, A Pediatric Perspective, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 1-6.
[3] Information about SOSORT and their guidelines can be found at http://www.sosort.mobi/index.php/en/
[4] Elisabetta D’Agata et al. Introversion, the prevalent trait of adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: an observational study Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders (2017) 12:27