Adult Scoliosis is technically any scoliosis case that exists either in those over 18, or those having reached skeletal maturity, either definition is valid but most scoliosis specialists would prefer the latter since we are focused more on the condition itself than an arbitrary point of “adulthood.”
There are two main types of adult scoliosis. Pre-existing adult scoliosis is essentially a case of scoliosis which is continuing from an earlier age (usually adolescent scoliosis). In adulthood, a continuing case of scoliosis typically becomes known as Adolescent Scoliosis in Adults or ASA. ASA can be discovered in adults of any age, but many ASA cases are already known from treatment earlier in life.
The second type is Degenerative De-Novo Scoliosis (sometimes noted as DDS) – this is the development of a new scoliosis case, usually as a result of spinal degeneration.
What causes Scoliosis in Adults?
ASA – that was scoliosis carried into adulthood from adolescence, isn’t caused in adulthood – it may or may not worsen depending on a number of factors, but the condition originated at an earlier point in life. Degenerative scoliosis is somewhat unusual in the scoliosis world since we understand its cause well – it’s due to wear and tear on the spine, but it is also strongly associated with a variety of conditions. Osteoporosis, degenerative disc disease, compression fractures and spinal canal stenosis have all been implicated in the development of degenerative scoliosis.
Since De-Novo scoliosis is a consequence of spinal degeneration with age, it rarely presents before 40 years of age – although, in patients with no known history of scoliosis, differentiation from degenerative idiopathic scoliosis may be difficult. It is thought that as many as 40% of over 60’s suffer from de-novo scoliosis[1], although a percentage of these cases will be undiscovered scoliosis from earlier in life. In fact, a good number of adult scoliosis cases are discovered through an investigation for another condition (such as back pain).
What is the prognosis and treatment for Adult Scoliosis?
ASA can be considered both stable (progression is very slow or non-existent) or unstable, progression is continuing. Whether an ASA case will progress quickly, slowly, or not at all may well depend on the size of the curve itself when adulthood is reached. Research has suggested that simply put, large curves tend to get worse – smaller curves may well be stable. Weinstein et al. and Ascani et al. have reported results showing that children with curves < 30° at skeletal maturity did not demonstrate curve progression into adulthood, while the majority of curves > 50° progress at approximately 1° per year.[2] The degree of progression will be the best guide for treating ASA cases – bracing, exercise or even just periodic monitoring could all be the right approach, depending on the case.
De-Novo scoliosis, being in many ways a consequence of time itself, always continues – however, the impact upon a persons life can be greatly minimised with the correct treatment. While postural deformity can be a major issue, one of the most commonly reported complaints arising from de-Novo scoliosis is pain – what’s more, a small increase in scoliosis could cause a large increase in pain, the deformity shifts the spine and pressure is applied to nerves.
The good news is that Recent advances in non-surgical treatment have shown significant improvement in terms of reduction of pain and symptoms in those with adult scoliosis. One approach involves the patient learning how to self-correct their abnormal posture, not just strengthen their lower back or core. The most effective approach would be the use of a customised brace, such as a ScoliBrace which helps to support the posture in a more comfortable position, pain is reduced (even with part-time bracing)[3] and quality of life is improved.
When non-surgical treatment is ineffective, surgery is often the only option, especially when leg pain becomes incapacitating and walking is almost impossible. Unfortunately, surgery at this stage is always complex and with significant risk. This is why it is important to find not only a good spinal surgeon but also one who specialises in scoliosis for the best possible outcome.
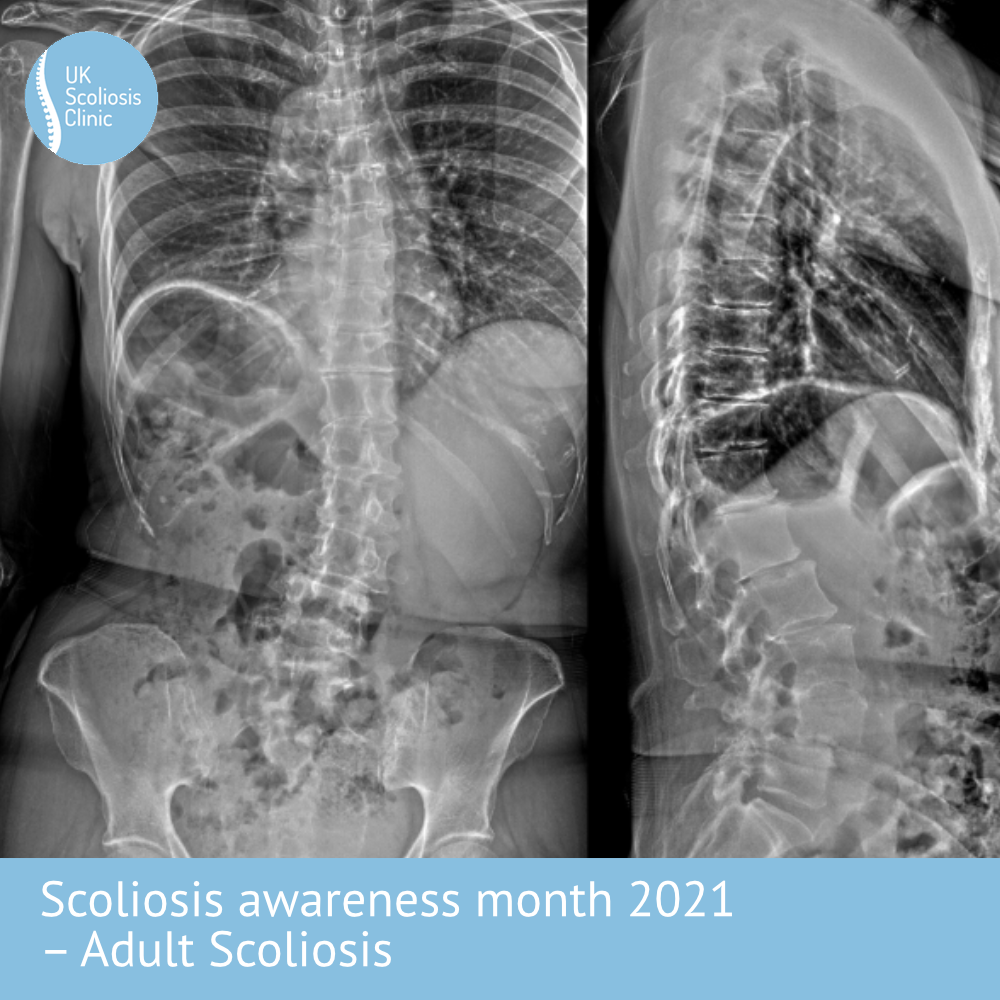
What does Adult Scoliosis look Like?
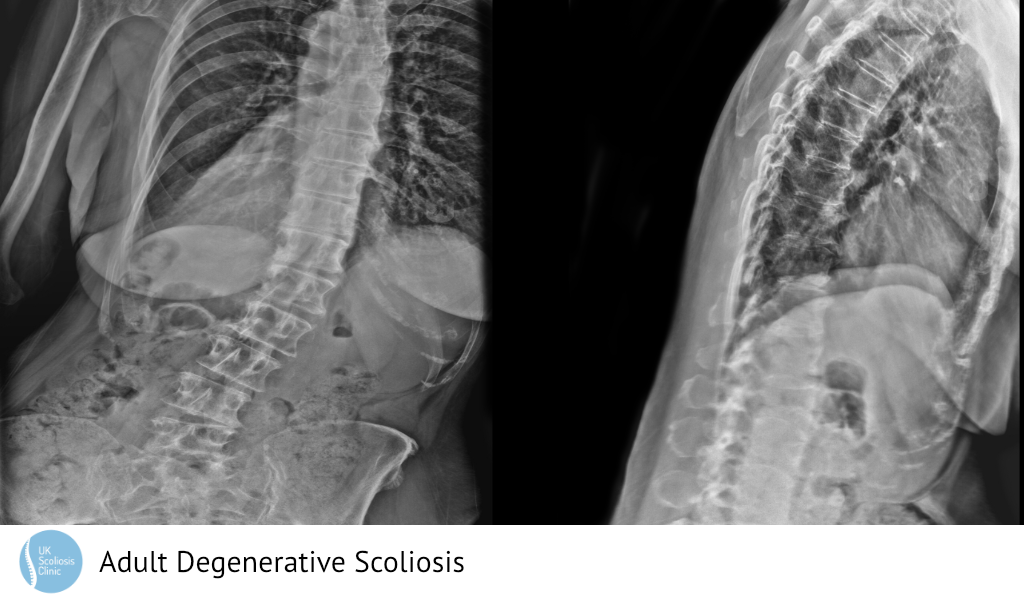
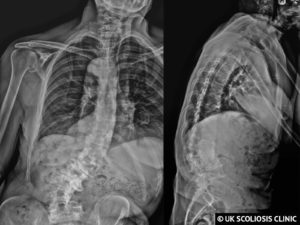
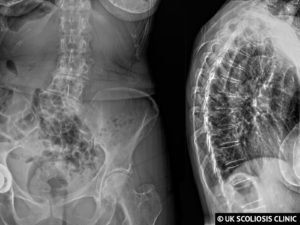
The below X-ray shows an example adult Scoliosis case. It’s usually not possible to tell how severe scoliosis is without taking an X-ray, although external signs can suggest that the condition may be present. This is why regular screening is so important!
[1] ‘Scoliosis in adults aged forty years and older: prevalence and relationship to age, race, and gender‘
Kebaish KM, Neubauer PR, Voros GD, Khoshnevisan MA, Skolasky R, Spine 2011 Apr 20;36(9):731-6.
[2] Weinstein SL, Ponseti IV: Curve progression in idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1983, 65:447-455.
Weinstein SL, Zavala DC, Ponseti IV: Idiopathic scoliosis: longterm follow-up and prognosis in untreated patients. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1981, 63:702-712.
Ascani E, Bartolozzi P, Logroscino CA, Marchetti PG, Ponte A, Savini R, Travaglini F, Binazzi R, Di Silvestre M: Natural history of untreated idiopathic scoliosis after skeletal maturity. Spine 1986, 11:784-789.
[3] Scoliosis bracing and exercise for pain management in adults—a case report Weiss et al, J Phys Ther Sci. 2016 Aug; 28(8): 2404–2407